About Oak's data
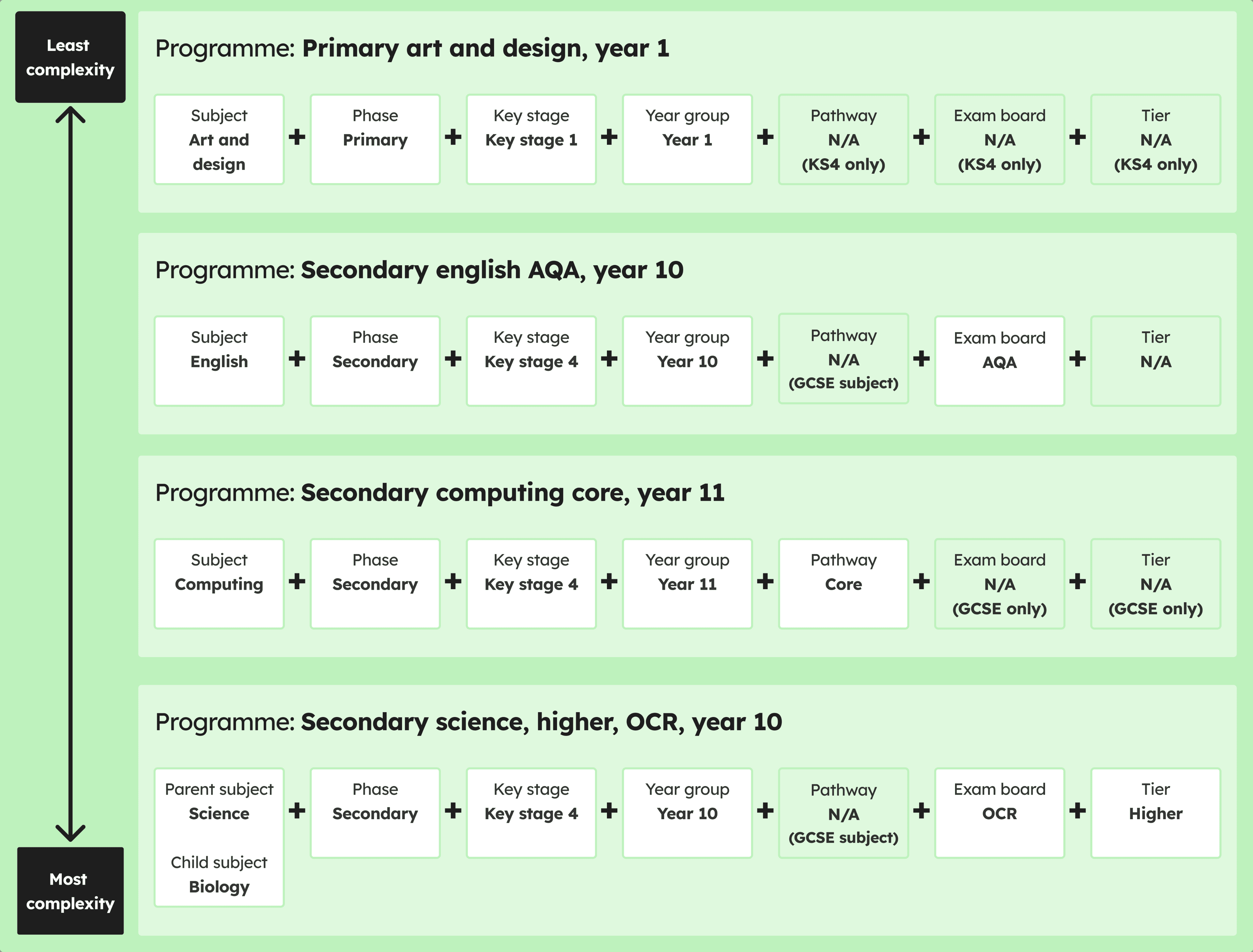
The programme examples in the diagram and programme factors that make them up, are listed below in complexity order (from least to most complex):
The programme factors for secondary english AQA, year 7 are:
The programme factors for secondary computing core, year 11 are:
Secondary science higher OCR, year 10 is one of the most complex programmes. The programme factors are:
A simple unit is one that includes a sequence of lessons that cover a specific topic.
For example, a year 2 design and technology unit called 'Wheels and axles: vehicles' has a sequence of 8 lessons that introduce the concept of wheels and axles through vehicle making.
Most units are simple units.
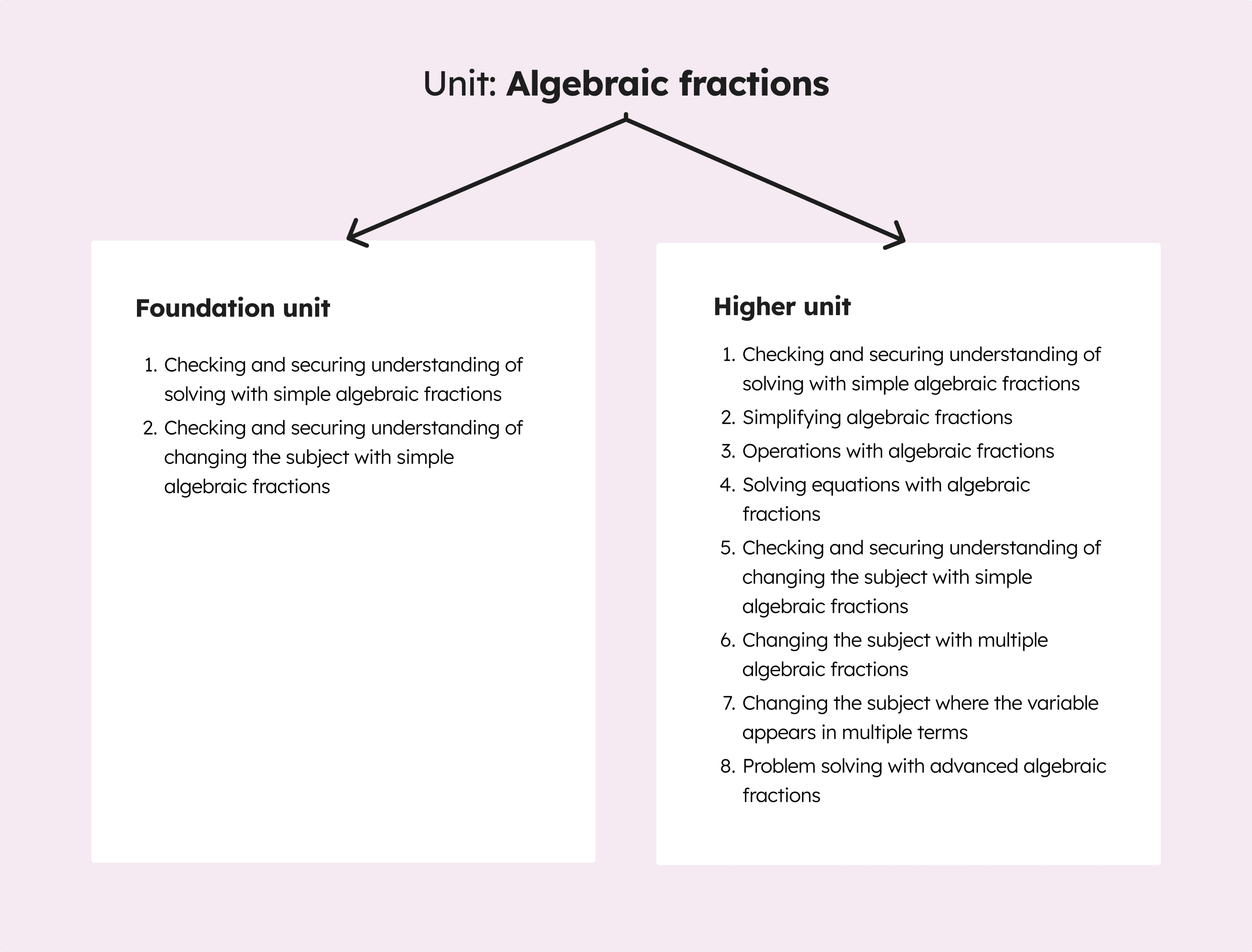
A variation on a unit. For example, a maths unit called ‘Algebraic fractions’ possesses a different sequence of lessons depending on the learning tier it is associated with.
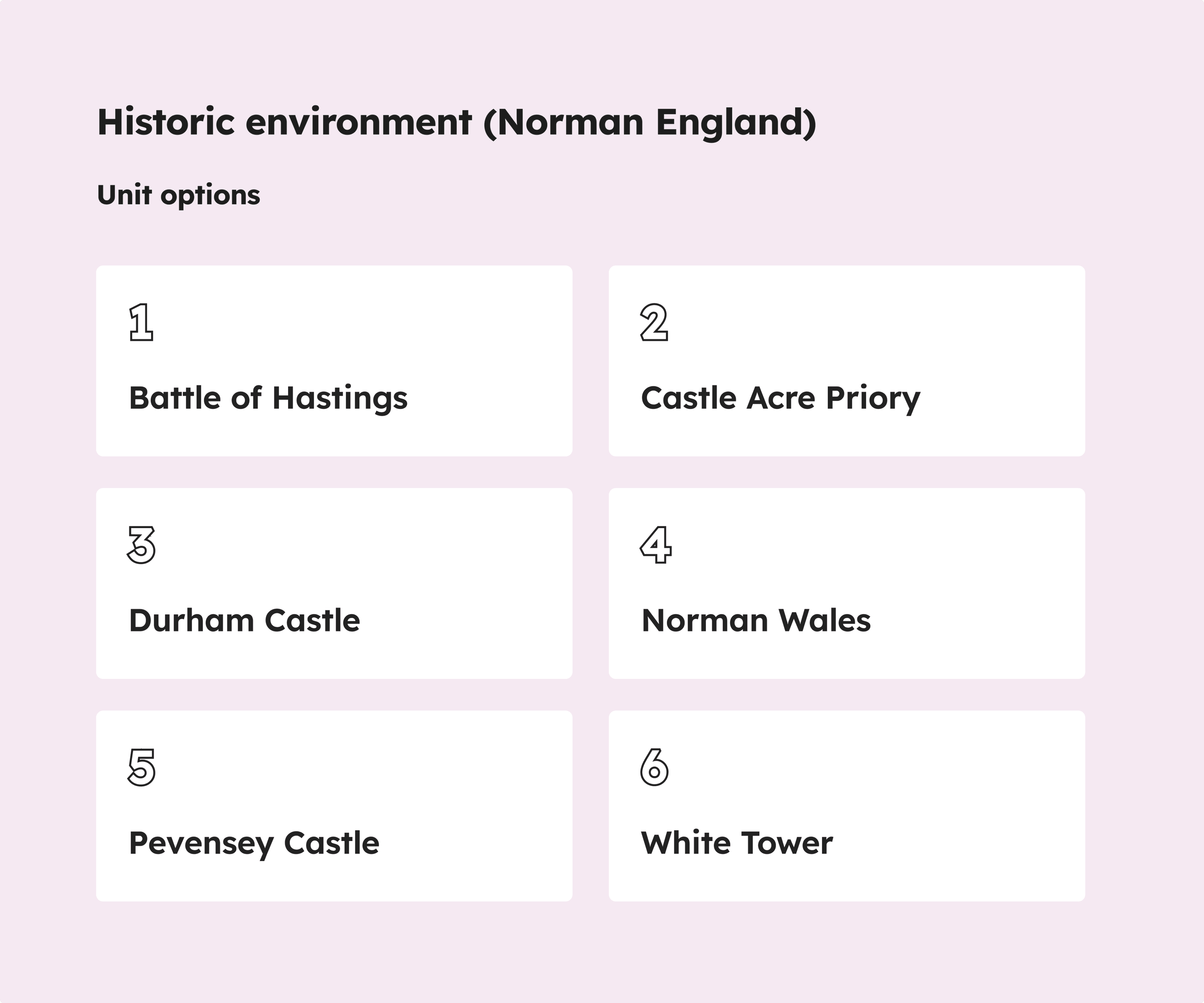
A unit with different options to allow teachers to personalise the content to their pupils’ needs. For example, a history unit called ‘Historic environment (Norman England)’ provides options depending on the event or landmark that the teacher feels would be most suitable for their pupils.
Threads can be used to group together units across the curriculum that build a common body of knowledge. Threads are important for making connections across year groups in each subject.
In Oak’s curriculum tool, users can highlight a thread in the filters to see which units sit in that thread across the full curriculum.

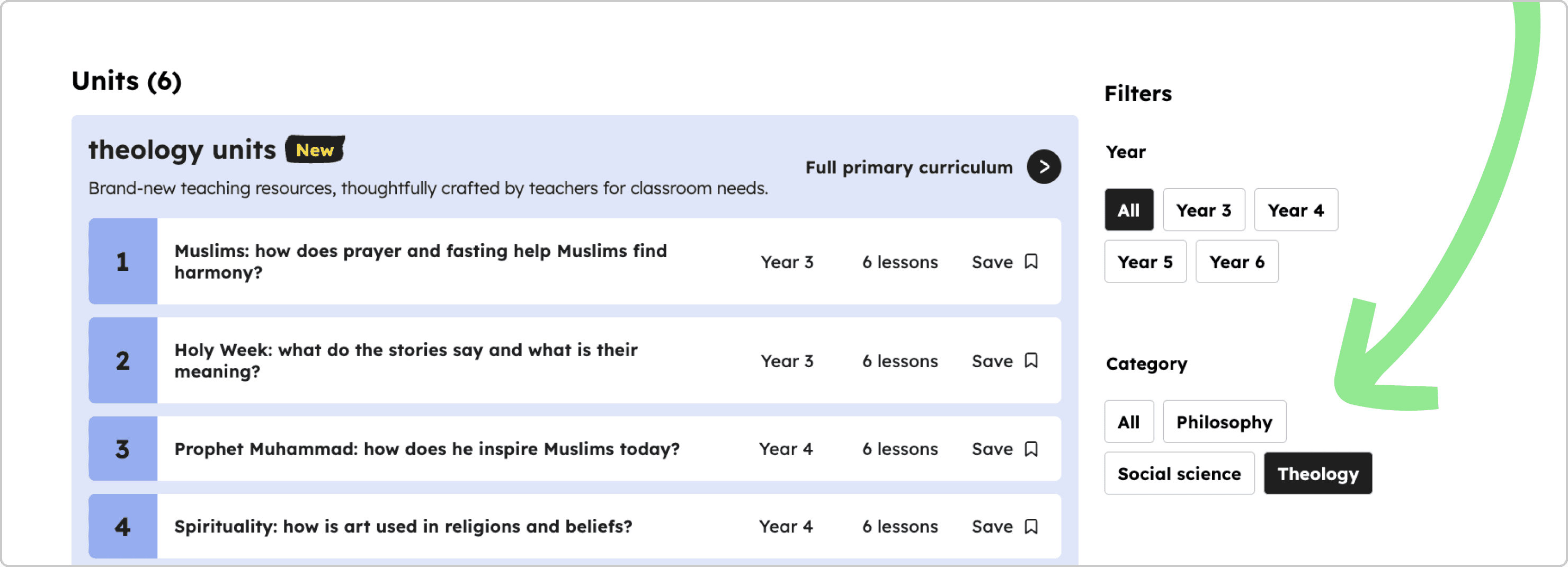
A well-established, high level division within a subject that helps filter and group units based on their content, signpost teachers, and provide a framework for the subject. Not all subjects will have subject categories. Currently, this applies to key stages 1-4 science, key stages 1, 2 and 4 English and key stages 1-3 religious education only.
In Oak’s lesson browse journey, subject categories are used as filters so that the user can refine the units displayed in the page.